Guidelines to run DNase-expression correlation method over BENGI benchmarks¶
Prerequisites¶
First we need to download the curated DNase counts from http://big.databio.org/papers/RED/supplement/ (see p. 14 of the BENGI paper).
Correlation-Methods/ └── Sheffield └── Signal-Matrices ├── dhs112_v3_int.bed ├── dhs112_v3_int.bed.gz └── exp112.bed
Partial reimplementation of Run-Sheffield.sh¶
First we make a copy of the Scripts folder downloaded from BENGI Github. We name it local_Scripts.
$ tree -L 2 . ├── Benchmark │ ├── All-Pairs.Fixed-Ratio │ ├── All-Pairs.Natural-Ratio │ ├── Annotations │ ├── README.md │ ├── Remove-Ambiguous-Pairs.Fixed-Ratio │ └── Remove-Ambiguous-Pairs.Natural-Ratio ├── Correlation-Methods │ └── Sheffield ├── Distance-Method │ └── Results ├── local_Scripts │ ├── Generate-Benchmark │ ├── Supervised-Methods │ └── Unsupervised-Methods ├── README.md └── Scripts ├── Generate-Benchmark ├── Supervised-Methods └── Unsupervised-Methods
Now we replace the content of local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods/Run-Sheffield.sh with the following:
#!/bin/bash ################# ## DEPENDENCIES # ################# # bedtools # python2 # scipy ################# ## INPUT ARGS: ## ################# # $1: `data`. Name of BENGI benchmark. Example: "GM12878.CHiC" # $2: `version`. Example: "v3" for BENGI with All pairs, Natural ratio # $3: `intermediate_output` relative_path to parent folder for intermediate results. # Folder need not exist yet. # WARNING: some inputs are not passed as args, see code below! ################# #### OUTPUT ##### ################# # els.bed: input `data` are intersected with ccREs that are involved in the BENGI # benchmarks. These ccREs are a subset of the ccREs with enhancer-like # signature for the cell type considered (+ they are distal - >2kb - from # any ENCODE-annotated TSS). After that, result is sorted and uniqued. # enhancer-matrix.bed # genes # genesFull # Inserm computer #workDir=~/Documents # Personal computer #workDir=~/Documents/INSERM # Genotoul workDir=/work2/project/regenet/workspace/thoellinger ccres=$workDir/BENGI/Benchmark/Annotations/hg19-cCREs.bed gnid_gname=/work2/project/regenet/workspace/thoellinger/BENGI/homo_sapiens.gnid.gnname.tsv # One must create the following repository before launching the script: signalDir=$workDir/BENGI/Correlation-Methods/Sheffield/ featureDir=$signalDir/Signal-Matrices # must contain DNase counts and gene expression # "dhs112_v3_int.bed", "exp112.bed" # see (http://big.databio.org/papers/RED/supplement/) data=$1 version=$2 intermediate_outputs_dir=$3 # All output that are not final results are # going to be stored here. Need not exist before launching the # script intermediate_outputs=$intermediate_outputs_dir/$data genes=$intermediate_outputs/genes # need not exist yet genesFull=$intermediate_outputs/genesFull # need not exist yet els=$intermediate_outputs/els.bed # need not exist yet enhancer_matrix=$intermediate_outputs/enhancer-matrix.txt # need not exist yet biosample=$(echo $data | awk -F "." '{print $1}') echo $biosample setDir=$workDir/BENGI/Benchmark/All-Pairs.Natural-Ratio train=$setDir/$data-Benchmark.$version.txt scriptDir=$workDir/BENGI/local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods # we modified the scripts found on BENGI Github outputDir=$signalDir/Results mkdir -p $outputDir mkdir -p $intermediate_outputs # dhs112_v3_int.bed (http://big.databio.org/papers/RED/supplement/) is space-delimited # so we first replace spaces by tabs. It contains the DNase counts over whole genome # for 112 cell types. # exp112.bed: idem. It contains the gene expressions for 112 cell types. if [[ ! -f $els ]]; then echo "Finding ccRE-dELS in input data..." awk 'FNR==NR {x[$1];next} ($5 in x)' $train $ccres | awk '{print $1 "\t" \ $2 "\t" $3 "\t" $5}' | sort -u > $els fi # WARNING: NOT ONLY THIS TASK MUST OBVIOUSLY BE RUN AT LEAST ON A NODE # BUT WE NEED TO ALLOCATE ENOUGH MEMORY TO PREVENT IT FROM BEING KILLED if [[ ! -f $featureDir/dhs112_v3_int_tab.bed ]]; then echo "dhs112 => dhs112_tab..." awk 'BEGIN{} {n=split($0, line, " "); ORS="\n"; print line[0]; ORS="\t"; for(u=1; u<n; u++){print line[u]}; ORS=""; print line[n]}' $featureDir/dhs112_v3_int.bed > $featureDir/dhs112_v3_int_tab.bed fi if [[ ! -f $enhancer_matrix ]]; then echo "Building enhancer matrix (DNase counts for all the input cell types) using bedtools... This can take several minutes..." bedtools intersect -wo -a $els -b $featureDir/dhs112_v3_int_tab.bed > $enhancer_matrix fi # enhancer-matrix.txt contains: # $1 to $4: enhancer infos, bed format # $5 to $7: for the current enhancer, chr, start and end of an overlapping DHS. # $8 to $(n_columns-1): respective DNase counts for all the 112 # cell types encountered in dhs112_v3_int_tab.bed # $n_columns: length (in bp) of the overlap if [[ ! -f $genes ]]; then echo "Finding all genes in input..." cat $train | awk '{print $2}' | sort -u > $genes fi if [[ ! -f $genesFull ]]; then echo "Computing gene list (<id> <name>)..." awk 'FNR==NR {x[$1];next} ($1 in x)' $genes $gnid_gname > $genesFull # warning: the python code has to be changed. See markdown. fi # we replaced `$stats` by NOTHING as we do not use this argument. if [[ ! -f $featureDir/exp112_tab.bed ]]; then echo "Adapting expression file format..." awk '{n=split($0, line, " "); ORS="\n"; if(NR==1){ORS=""}; print line[0]; ORS="\t"; for(u=1; u<n; u++){print line[u]}; ORS=""; print line[n]}' $featureDir/exp112.bed > $featureDir/exp112_tab.bed fi echo "Running python script... This can take several minutes..." python $scriptDir/sheffield.correlation.py $featureDir/exp112_tab.bed $genesFull $enhancer_matrix NOTHING $train $biosample |sort -t $'\t' -k 5,6 > $outputDir/$data-Correlation.$version.txt
Partial reimplementation of sheffield.correlation.py¶
We replace the content of local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods/sheffield.correlation.py with the following (do not pay too much attention to comments, some of them may be inaccurate):
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sys, scipy, math from scipy import stats import numpy as np # to reconstruct statDict "by hand" from itertools import groupby # We use all_equal to prevent a division-by-zero error in Calculate_Correlation def all_equal(iterable): g = groupby(iterable) return next(g, True) and not next(g, False) def Process_Biosample(biosample): biosampleDict={"GM12878":28, "HeLa":50, "K562":88,"HMEC":59,"NHEK":100} if biosample in biosampleDict: return biosampleDict[biosample] else: return "no" def Calculate_Correlation(array1, array2): if not (all_equal(array1) or all_equal(array2)): stat=stats.pearsonr(array1, array2)[0] else: stat = float('NaN') return stat def Create_Gene_Dict(genes): geneDict={} genes.next() #skips header for line in genes: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") geneDict[line[3]]=[float(i) for i in line[5:]] return geneDict def Create_ELS_Dict(els, column): elsDictA={} elsDictB={} for line in els: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") if column == "no": score=max(float(i) for i in line[7:-1]) else: score=float(line[column]) if line[3] not in elsDictA: elsDictA[line[3]]=[float(line[-1]),score] # [size of overlap, counts fot the cell type considered] elsDictB[line[3]]=[float(i) for i in line[7:-1]] # [size of overlap, [counts for all cell types]] elif elsDictA[line[3]][0] < float(line[-1]): # See comment below first. Here, same kind of thing, but it is about maximizing the overlap. # Note that first the overlap is maximized, and only then the counts are maximized. # This has Shuge implications: if there are 1000 counts for a candidate enhancer with which the # overlap is 149, and at best 3 counts for enhancers with overlap 150, the ones with overlap 150 and 3 # counts only are kept... # To prevent such a "side effect", one may replace the following "elif" with an "if" # I personnaly think this side effect is undesirable, but here we keep the "elif" # to obtain the same results as Moore et al. elsDictA[line[3]]=[float(line[-1]),score] elsDictB[line[3]]=[float(i) for i in line[7:-1]] elif elsDictA[line[3]][1] < score: # note that all peak widths are 150 # if counts for another open chromatin region overlapping this enhancer has already been written, # but are fewer than for the current open chromatin region overlapping this same enhancer, # then we overwrite the counts with these new ones. # At the end of the day, this results in taking into account, for each enhancer, only the open chromatin # region that maximize the counts of DNase over a given enhancer ; although the selection is made among # regions that maximize the overlap only, see comment above. elsDictA[line[3]]=[float(line[-1]),score] elsDictB[line[3]]=[float(i) for i in line[7:-1]] # Well at the end of the day, elsDictB[key="enhancer id"] = [max overlap with a DHS, max counts in this DHS] return elsDictB, elsDictA def Create_Symbol_Dict(symbols): symbolDict={} for line in symbols: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") symbolDict[line[0]]=line[1] return symbolDict def Create_Stat_Dict(stats): # For now we know that: # stat (argv[4]) must contain at least 3 columns # first column is a gene id (see for loop at the end of the code) # 2nd and 3rd columns are float / real numbers. # Both are later compared to correlations. statDict={} for line in stats: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") statDict[line[0].rstrip()]=[float(line[1]),float(line[2])] return statDict genes=open(sys.argv[1]) # gene expression geneDict=Create_Gene_Dict(genes) genes.close() # geneDict[key = "gene NAME (not id)"] = [expression in cell line 1, expression in cell line 2, etc] symbols=open(sys.argv[2]) # gene annotation symbolDict=Create_Symbol_Dict(symbols) symbols.close() column=Process_Biosample(sys.argv[6]) # the correct column is 28 for GM12878 els=open(sys.argv[3]) # ccRE expression elsDict, test =Create_ELS_Dict(els,column) els.close() # elsDict[key="enhancer id"] = [max overlap of this enhancer with a DHS, max counts for this max overlap] # For now we try to rebuild statArray directly in this script. #stat=open(sys.argv[4]) #statArray = Create_Stat_Dict(stat) #stat.close() # On essaye ci-dessous # On le fait volontairement d'une maniere très peu optimisée, c'est juste pour tester, en évitant d'induire d'autres sources # potentielles de problèmes pairs=open(sys.argv[5]) # BENGI benchmark all_cor = {} for line in pairs: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") els=line[0] # candidate enhancer id gene=symbolDict[line[1].rstrip()] # name (not id) of candidate paired gene if els in elsDict and gene in geneDict: if gene in all_cor: all_cor[gene].append(Calculate_Correlation(elsDict[els],geneDict[gene])) else: all_cor[gene] = [Calculate_Correlation(elsDict[els],geneDict[gene])] pairs.close() # Now for each gene name of gene id found in the benchmark pairs, all_cor[gene] should # be the list of the correlations of its expression accross all cell lines, with # the counts of DNase accross all cell lines, for enhancers it is paired with pairs=open(sys.argv[5]) # BENGI benchmark statArray = {} for line in pairs: #inutile il suffit de boucler sur tous les genes trouves, une seule fois chacun, qu'on aurait du enregistrer precedemment deja line=line.rstrip().split("\t") els=line[0] # candidate enhancer id gene=symbolDict[line[1].rstrip()] # name (not id) of candidate paired gene if els in elsDict and gene in geneDict: if gene not in statArray: statArray[gene] = [np.mean(all_cor[gene]), np.std(all_cor[gene])] pairs.close() pairs=open(sys.argv[5]) # BENGI benchmark for line in pairs: line=line.rstrip().split("\t") els=line[0] # candidate enhancer gene=symbolDict[line[1].rstrip()] # name (not id) of candidate paired gene if els in elsDict and gene in geneDict: cor=Calculate_Correlation(elsDict[els],geneDict[gene]) # correlation between counts of DNase over els and gene expression accross the 112 biosamples # cor est la corrélation entre les counts max de DNase sur els, et l'expression du gène appairé avec cet els. # On a dit que : # statArray devait être issu d'un fichier de trois colonnes qui est tel que : # La clef est un id de gene (visiblement plutôt un NOM de gène ! - pourquoi pas...) # La première valeur est, pour chaque gène, la corrélation moyenne qu'on trouve entre ce gène et les ccRE auxquels il est appairé # La deuxième valeur est, pour chaque gène, l'écart-type de ces mêmes corrélations. if math.isnan(cor): cor=0 if statArray[gene][1] != 0: Z=(cor-statArray[gene][0])/statArray[gene][1] else: Z=0 p=stats.norm.sf(abs(Z))*2 print line[2], "\t", cor, "\t", p, "\t", Z, "\t", els, "\t", line[1] else: pass print line[2], "\t", -100, "\t", 1, "\t", -100, "\t", els, "\t", line[1]
Running the code for BENGI benchmarks over GM12878¶
If working on Genotoul, start with:
conda activate base && conda activate abcmodel && conda activate py2 && module load bioinfo/bedtools-2.27.1
and before launching the script, do not forget (a lot of memory is required):
srun --mem=32G --pty bash
Now it suffices to run Run-Sheffield.sh over the six benchmarks:
./local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods/Run-Sheffield.sh GM12878.CHiC v3 Correlation-Methods/Sheffield
$ ./local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods/Run-Sheffield.sh GM12878.CHiC v3 Correlation-Methods/Sheffield GM12878 Finding ccRE-dELS in input data... Building enhancer matrix (DNase counts for all the input cell types) using bedtools... This can take several minutes... Finding all genes in input... Computing gene list (<id> <name>)... Running python script... This can take several minutes...
./local_Scripts/Unsupervised-Methods/Run-Sheffield.sh GM12878.GEUVADIS v3 Correlation-Methods/Sheffield
etc.
Resulting in the following:
Correlation-Methods/ └── Sheffield ├── GM12878.CHiC │ ├── els.bed │ ├── enhancer-matrix.txt │ ├── genes │ └── genesFull ├── GM12878.CTCF-ChIAPET │ ├── els.bed │ ├── enhancer-matrix.txt │ ├── genes │ └── genesFull ... # same for the 4 others benchmarks ├── Results │ ├── GM12878.CHiC-Correlation.v3.txt │ ├── GM12878.CTCF-ChIAPET-Correlation.v3.txt │ ├── GM12878.GEUVADIS-Correlation.v3.txt │ ├── GM12878.GTEx-Correlation.v3.txt │ ├── GM12878.HiC-Correlation.v3.txt │ └── GM12878.RNAPII-ChIAPET-Correlation.v3.txt └── Signal-Matrices ├── dhs112_v3_int.bed ├── dhs112_v3_int.bed.gz ├── dhs112_v3_int_tab.bed ├── exp112.bed └── exp112_tab.bed
Analysis with R¶
Code¶
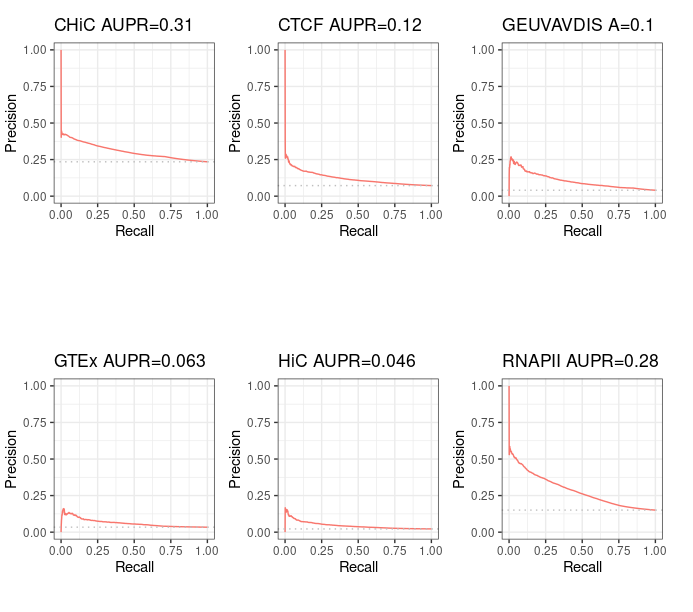
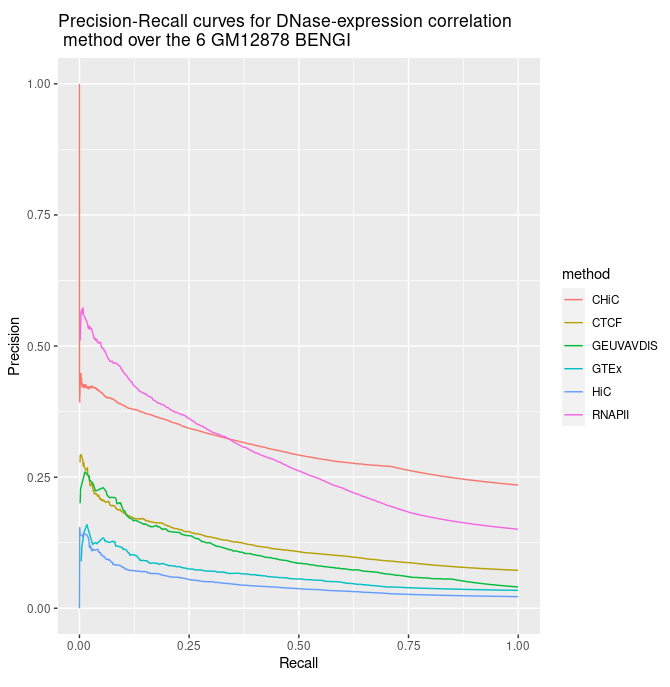
--- title: "BENGI Rank Distance evaluation" date : "décembre 2020" output: md_document #html_document: #toc: true #toc_float: true #toc_depth : 4 #number_sections : true --- ```{css,echo=F} .badCode { background-color: #C9DDE4; } ``` ```{r setup, echo=FALSE, cache=FALSE} library(knitr) ## Global options options(max.print="75") opts_chunk$set(echo=TRUE, cache=FALSE, prompt=FALSE, tidy=TRUE, comment=NA, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, class.source="badCode") opts_knit$set(width=75) ``` ```{r} library(ggplot2) library(ggpubr) # for ggarrange library(dplyr) # for bind_rows # Tools for precision-recall : (see https://classeval.wordpress.com/tools-for-roc-and-precision-recall/) library(precrec) #library(ROCR) #library(pROC) #library(PRROC) ``` ```{r, results="hide"} rm(list = ls()) # Personal work_dir = "~/Documents/INSERM/" # Inserm #work_dir = "~/Documents/" path_to_results = paste(work_dir, "BENGI/Correlation-Methods/Sheffield/Results/", sep='') #file_names = c("GM12878.CHiC-Correlation.v3.txt") file_names = c("GM12878.CHiC-Correlation.v3.txt", "GM12878.CTCF-ChIAPET-Correlation.v3.txt", "GM12878.GEUVADIS-Correlation.v3.txt", "GM12878.GTEx-Correlation.v3.txt", "GM12878.HiC-Correlation.v3.txt", "GM12878.RNAPII-ChIAPET-Correlation.v3.txt") #short_names = c('CHiC') short_names = c('CHiC', 'CTCF', 'GEUVAVDIS', 'GTEx', 'HiC', 'RNAPII') nb_files = length(file_names) colnames <- c('interaction', 'cor', 'p', 'Z', 'ccRE', 'gene') results <- sapply(file_names, simplify=FALSE, function(file_name){ Df <- read.table(paste(path_to_results, as.character(file_name), sep=''), sep='\t') Df[[1]] <- factor(Df[[1]], levels=c(0,1), labels=c("no interaction", "interaction")) names(Df) <- colnames return(Df) }) names(results) <- short_names #library(dplyr) All_results <- bind_rows(results, .id = 'method') # requires library(dplyr) ``` ```{r} str(results) summary(results$CHiC) ``` ```{r} ggplot(aes(y = cor, x = method, fill = interaction), data = All_results) + geom_boxplot() ``` ```{r} sscurves_dnase_expression <- list() sscurves_dnase_expression <- sapply(results, simplify=FALSE, function(Df){ evalmod(scores = Df$cor, labels = Df$interaction) # comes with "precrec" library }) ``` ```{r} #library(ggplot2) p1 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[1]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[1], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[1]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " AUPR=")) p2 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[2]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[2], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[2]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " AUPR=")) p3 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[3]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[3], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[3]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " A=")) p4 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[4]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[4], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[4]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " AUPR=")) p5 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[5]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[5], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[5]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " AUPR=")) p6 <- autoplot(sscurves_dnase_expression[[6]], curvetype = c("PRC")) + ggtitle(paste(short_names[6], signif(attr(sscurves_dnase_expression[[6]], 'auc')[[4]][2], digits=2), sep = " AUPR=")) # ggarrange comes with library('ggpubr') figure <- ggarrange(p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, ncol = 3, nrow = 2) figure ``` Alternatively we can plots all Precision - Recall curves on the same graph. ```{r} all_sscurves_dnase_expression <- sapply(sscurves_dnase_expression, simplify = FALSE, function(obj){ Df <- data.frame(obj$prcs[[1]]$x, obj$prcs[[1]]$y) names(Df) <- c('x', 'y') return(Df) }) all_sscurves_dnase_expression <- bind_rows(all_sscurves_dnase_expression, .id = 'method') total_nrow = nrow(all_sscurves_dnase_expression) max_nb_points_to_plot = 20000 if(total_nrow>max_nb_points_to_plot){ set.seed(1) samples_points = sample(1:total_nrow, min(max_nb_points_to_plot, total_nrow), replace=TRUE) } else{ samples_points = 1:total_nrow } ggplot(aes(y = y, x = x, color = method), data = all_sscurves_dnase_expression[samples_points,]) + geom_line() + ylim(0,1) + xlab('Recall') + ylab('Precision') + ggtitle("Precision-Recall curves for DNase-expression correlation\n method over the 6 GM12878 BENGI") ```
Results¶